Everything You Need to Know About First-Party Data
In today’s privacy-first digital landscape, understanding first-party data has become crucial for businesses seeking to establish meaningful customer relationships while complying with evolving regulations. First-party data is information that companies collect directly from their customers through their own channels, making it the most valuable and reliable data source available to modern marketers.
As third-party cookies disappear and privacy laws tighten, businesses that master 1st party data collection and activation will have a significant competitive advantage.
What Is First-Party Data? (Definition & Examples)
First-party data is the goldmine your business collects directly from customers through your website, app, emails, social media, purchases, and surveys. Unlike third-party data, it comes straight from the source: real interactions with your audience.
Every form filled, purchase made, or newsletter subscription adds valuable insights like email addresses, buying habits, and product preferences. Best of all, this data belongs exclusively to you, giving your business a powerful edge.
Types of First-Party Data
Businesses collect several categories of first-party data across customer touchpoints:
Behavioral Data
This captures how customers interact with your digital properties. It includes website navigation patterns, pages visited, time spent on site, content downloads, video views, and feature usage in apps. Behavioral data reveals what customers are interested in and how they engage with your brand.
Transactional Data
Purchase history, order values, frequency of purchases, payment methods, abandoned carts, and refund requests fall into this category. Transactional data provides concrete insights into customer buying patterns and lifetime value.
Demographic Data
Information like age, gender, location, job title, company size, and industry helps you understand who your customers are. This data typically comes from account registration forms, profile updates, and customer onboarding processes.
Engagement Data
Email open rates, click-through rates, social media interactions, event attendance, webinar participation, and customer service conversations measure how actively customers engage with your communications and offerings.
Why First-Party Data Is Important
The shift toward first-party data isn’t just a trend—it’s a fundamental change in how businesses understand and reach their audiences.
Privacy Compliance
With regulations like GDPR and CCPA reshaping data collection practices, first-party data offers a compliant path forward. When customers willingly share information directly with your brand, you have clear consent and transparency about how their data will be used.
Accuracy and Reliability
Because you collect first-party data directly from your customers, it’s more accurate and trustworthy than information obtained through intermediaries. There’s no telephone game distorting the data as it passes through multiple hands.
Competitive Advantage
Your first-party data is unique to your business. Competitors can’t access the same insights about your specific customer relationships, preferences, and behaviors. This exclusivity makes it incredibly valuable for differentiation.
Personalization at Scale
First-party data enables you to create highly personalized experiences across channels. From tailored product recommendations to customized email content, you can use what customers have directly told you to serve them better.
Cost Efficiency
While third-party data requires ongoing purchases, first-party data is an asset you build over time. The infrastructure investment pays dividends as your data collection improves and your audience grows.
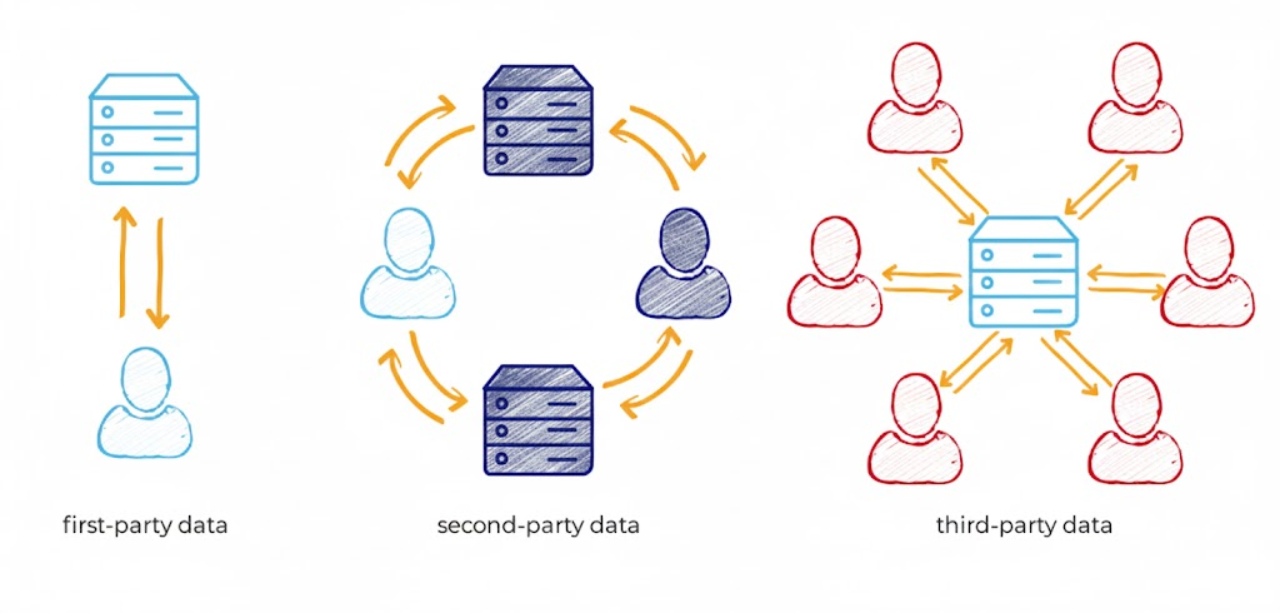
First-Party vs Second-Party vs Third-Party Data
To master the data landscape, know the three types:
- First-party data comes directly from your audience via owned channels—highly relevant, consent-based, and fully yours.
- Second-party data is another company’s first-party data shared through partnerships—reliable, but less tailored.
- Third-party data is aggregated and sold by providers without direct customer ties. It’s widely available, but declining in value due to privacy concerns and reduced accuracy.
How Businesses Collect First-Party Data
Smart companies build systematic approaches to gathering first-party data across touchpoints:
Website Analytics
Tools like Google Analytics track visitor behavior, traffic sources, page performance, and conversion paths. Implementing proper tracking reveals how prospects discover and navigate your site.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
Your CRM centralizes customer interactions, sales history, support tickets, and communication preferences. Every touchpoint becomes a data collection opportunity that builds a comprehensive customer profile.
Email Marketing Platforms
Subscription forms, campaign engagement metrics, preference centers, and click behavior all generate valuable first-party data about what content resonates with your audience.
Mobile Applications
In-app behavior, feature usage, session duration, push notification responses, and location data (with permission) provide rich insights into how customers interact with your mobile experience.
E-commerce Platforms
Purchase transactions, product reviews, wishlist additions, cart abandonment, and browsing history create a detailed picture of customer preferences and intent.
Surveys and Feedback Forms
Direct customer feedback through post-purchase surveys, NPS questionnaires, customer satisfaction ratings, and product feedback requests gives you explicit insights into customer sentiment.
Social Media Channels
Owned social profiles capture follower demographics, engagement patterns, direct messages, and content preferences that complement data from other channels.
Examples of First-Party Data in Action
Leading companies leverage first-party data to drive results across business functions:
Personalized Marketing Campaigns
An online retailer uses purchase history and browsing behavior to send targeted product recommendations. Customers who bought running shoes receive emails about complementary athletic wear, increasing conversion rates by showing relevant products.
Dynamic Website Content
A SaaS company customizes homepage content based on visitor industry and company size (collected during previous visits or form submissions). Enterprise visitors see case studies from Fortune 500 companies, while small business visitors see pricing designed for their needs.
Retargeting and Nurturing
A B2B software provider tracks which features prospects explore during free trials. Sales teams receive alerts when high-intent behaviors occur, enabling timely, relevant outreach that addresses specific interests.
Customer Retention
An e-commerce subscription service analyzes purchase frequency patterns to identify customers at risk of churning. Automated retention campaigns with special offers deploy before subscriptions lapse.
Product Development
A mobile app company analyzes feature usage data to prioritize roadmap decisions. Features with high engagement receive enhancements, while rarely-used features are reconsidered or redesigned.
Best Practices for Using First-Party Data
To unlock the full value of first-party data, focus on strategy and trust:
- Set clear governance and quality standards for accuracy.
- Be transparent with customers—privacy and consent build confidence.
- Centralize data in a customer data platform (CDP) for a unified customer view.
- Prioritize security to protect customer information.
- Capture core data (emails, purchases, engagement) before advanced tracking.
- Audit regularly to clean and update records.
- Turn data into actionable insights that drive better decisions and experiences.
Future of First-Party Data
As the internet shifts to a cookieless, privacy-first era, first-party data becomes the cornerstone of customer insight. With third-party cookies fading, businesses must rely on owned channels to understand and serve their audiences.
Contextual targeting, on-site personalization, and privacy-enhancing technologies are redefining engagement. AI and machine learning unlock predictive power from your data, while zero-party data—customers willingly sharing preferences—adds even deeper understanding. Companies that master these strategies will gain a decisive edge in the new data-driven landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes first-party data better than third-party data?
First-party data is more accurate because it comes directly from your customers, provides unique competitive insights that only your business can access, ensures privacy compliance since customers share it willingly with your brand, and costs less over time since you’re building an owned asset rather than repeatedly purchasing external data.
How can small businesses start collecting first-party data?
Begin with email subscriptions using lead magnets like guides or discounts to build your list. Implement basic website analytics to understand visitor behavior. Create customer accounts that incentivize registration with exclusive benefits. Use simple surveys to gather customer preferences and feedback. These foundational approaches require minimal investment but generate valuable data.
Is first-party data enough for effective marketing?
While first-party data should form the foundation of your marketing strategy, it works best when complemented by strategic second-party partnerships and contextual signals. The key is making first-party data your primary source while selectively augmenting it with privacy-compliant additional sources that fill specific gaps.
How long should businesses retain first-party data?
Retention periods depend on regulatory requirements, business needs, and customer expectations. Generally, keep active customer data as long as the relationship continues and for a reasonable period afterward for reactivation opportunities. Archive or delete data for customers who haven’t engaged in 2-3 years unless regulations or legitimate business interests require longer retention. Always allow customers to request data deletion.
READ ALSO:- Understanding Ad-Tech
Conclusion
First-party data represents the future of customer understanding in an increasingly privacy-conscious digital world. By collecting information directly from your audience through owned channels, you build a valuable, compliant, and exclusive asset that drives personalization, improves customer experiences, and generates sustainable competitive advantage.
The businesses that thrive in the coming years will be those that view first-party data not as a compliance requirement but as a strategic opportunity. Start building your first-party data infrastructure today by improving data collection across touchpoints, centralizing customer information, and using those insights to serve your audience better.
The transition away from third-party data isn’t a challenge to overcome—it’s an invitation to build stronger, more transparent relationships with the customers who matter most to your business.
Related Articles
Continue your learning journey with these related insights
What’s the Difference Between AdTech and MarTech?
In today’s digital-first world, marketing success depends heavily on technology. Two terms you’ll hear constantly are MarTech and AdTech. While they often work together, they serve very different purposes. Understanding the differences between martech and adtech is essential for building effective marketing strategies, enhancing customer experience, and maximizing return on investment (ROI). This guide explains […]
How AI Uses Harmonized Ad Data to Optimize Campaigns
Digital advertising wastes billions every year. Poor timing, wrong audiences, and scattered data are the main problems. AI fixes this by combining data from all your platforms into one smart system that actually works. What Is Harmonized Ad Data? Harmonized ad data means combining information from all your advertising platforms into one place. Instead of […]
Ready to Transform Your Advertising Strategy?
Join thousands of advertisers who trust Performoo to optimize their campaigns and maximize revenue.